In this article, you will learn about wastewater treatment, methods of wastewater treatment, and various terms used in the wastewater treatment process.
Table of Contents
What Is Wastewater Treatment?
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from sewage or wastewater and convert it into effluent and that can be returned to the water table with minimum impact on the environment or can be directly reused.

Wastewater treatment is an important initiative that has to be taken more seriously for the betterment of our future and for the water table.
There are three stages of the wastewater treatment process, primary water treatment, secondary water treatment, and tertiary water treatment.
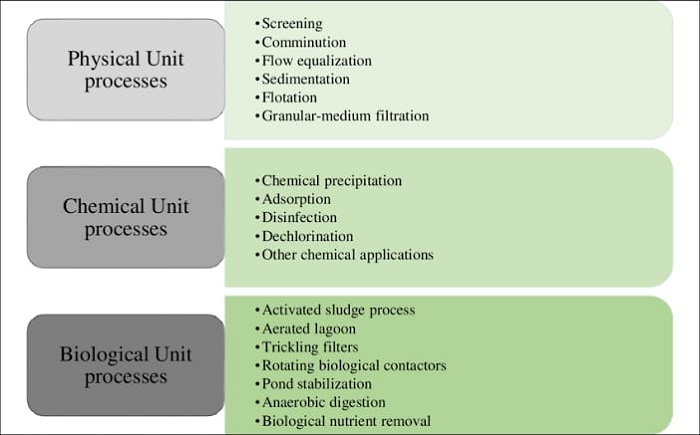
Methods Of Wastewater Treatment:
There are four very effectively used processes of treating wastewater:
- Physical water treatment
- Chemical water treatment
- Biological water treatment
- Sludge treatment
1. Physical Water Treatment:
In this process, the solids from water are removed by sedimentation, skimming, screening. There is no use of chemicals required in this process.
The main techniques of physical wastewater treatment include sedimentation, which suspends the heavy particles/insoluble from the water. Once the insoluble material settles down we can separate the pure water.
Aeration is also one of the other physical water treatment techniques. In which the air is circulated through the water to provide oxygen to it. Filtration is the third method that is used to filter out all the contaminants. The most common type is sand filter it can remove the grease found on the surface of wastewater and can also be removed by this method.
2. Chemical Water Treatment:
Chemicals are used for the treatment of water in this process. To kill bacteria chlorine is commonly used as an oxidizing chemical and decomposes water by adding contaminants into it. Ozone is also another of oxidizing agent used for purifying the wastewater. To bring the water to a pH of 7 neutralization is another process.
3. Biological Water Treatment:
In this process of treatment organic matter present in wastewater, such as human waste, soap, oils, and foods can break down. In biological treatment, microorganisms metabolize organic matter in wastewater
Biological treatment can be further divided into three categories:
- (I) Aerobic Process:
- (II) Anaerobic Process:
- (III) Composting:
(I) Aerobic Process:
The organic matter is decomposed by bacteria and converted into CO (Carbon monoxide) which can be used by plants. This process uses oxygen.
(II) Anaerobic Process:
Here, Fermentation is used to ferment the waste at a specified temperature. This process does not use oxygen.
(III) Composting:
It is a type of Aerobic process where wastewater is treated with a mix of dust or carbon elements.
Secondary treatment removes most of the solids present in wastewater, other solid nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus remain in the water.
4. Sludge Treatment:
Sludge treatment is the solid-liquid separation process where there is the least requirement of residual moisture in the solid phase and the very lowest solid particle residues are required in the separation of the liquid phase.
What is a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
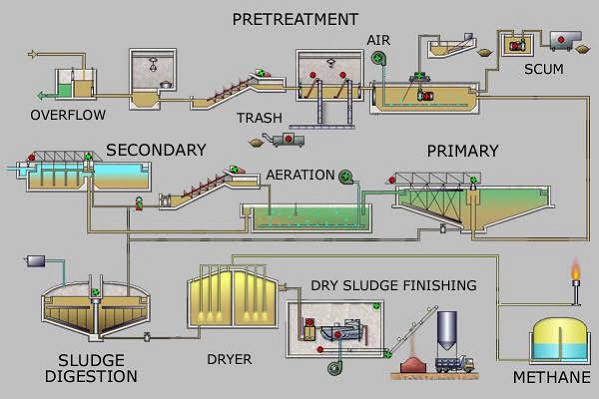
Sewage treatment plant or STP or domestic wastewater treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and household i.e runoff and domestic. It includes chemical, physical, and biological processes to remove chemical, physical, and biological contaminants respectively.
STPs’ main objective is to produce a waste stream (treated effluent) and a solid waste or sludge suitable to reuse back into households.
Materials such as trash, tree limbs, leaves, plastic bottles, etc, are removed from the raw wastewater so that it cannot damage or clog the skimmers or pumps and this process is pre-treatment.
All large objects in the influent sewage water are strained to remove in the sewage stream. and is most commonly done by an automated mechanically raked bar screen serving large populations, whereas in the old or smaller a manually cleaning screen may be used and this process is called screening.
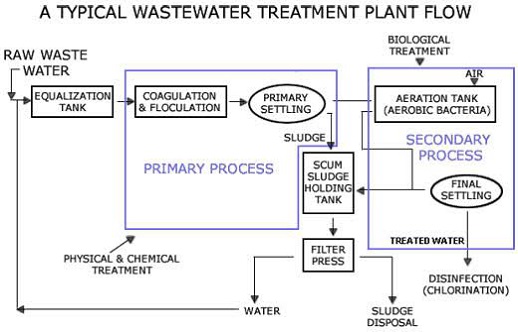
Primary Treatment:
Sewage flows through the large tanks commonly known as primary clarifiers or primary sedimentation tanks. Tanks are larger in shapes in which sludges settle down and floating material such as grease and oils can rise to the surface and be skimmed off. The main purpose of the primary sedimentation stage is to get both liquids that are homogenous and can be biologically treated and can separately treat sludge.
Secondary Treatment:
To degrade the biological content of sewage which is formed by human waste, food waste, grease, detergents are treated in secondary treatment. Most of the municipal plants use to treat the settled liquid sewage using biological processes. For the process to be effective the plant and life require both oxygen and a surface on which to live.
Secondary treatment systems are classified as fixed-film or suspended growth. The fixed-film system treatment process includes rotating biological contractors and trickling filters where on media biomass grows and on its surface sewage passes by. In suspended growth systems, such as activated sludge, the biomass is well mixed with sewage and in smaller space, it can be operated than the fixed-film system which treats the same amount of water.
Activated Sludge:
Activated sludge plants process that uses dissolved oxygen to promote the growth of biological floe that removes organic material. in which process traps particulate and can, convert ammonia to nitrate and nitrate to nitrogen gas.
Combined Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP):
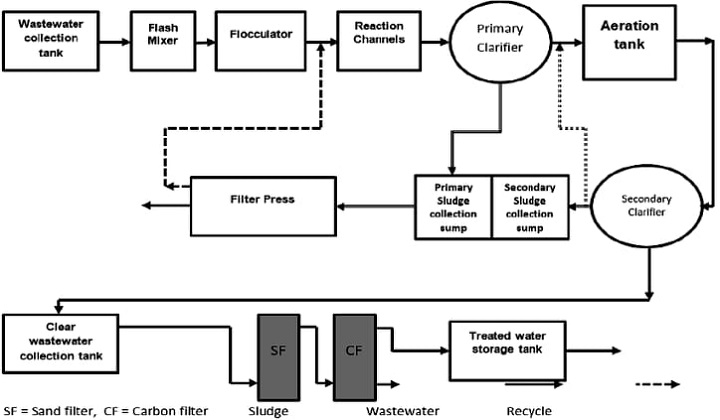
There are lots of SSI small-scale industries that are unable to put the treatment systems thus to benefit these industries concept of CETP is introduced so that industries can treat their effluent before disposal whether it is in sewage, lakes, ponds, rivers, etc. CETP is set up in that location where there is a cluster of Small scale industries are located. In USA, ministry of environment and forest sponsored a scheme centrally namely CETP in order to curb pollution especially to treat the effluent discharging from many Small scale industries. So the main objective of CEPT is to reduce the treatment cost which is carried by the individual unit to the maximum while protecting the water environment to the maximum. Thus the design and technical specifications of making CEPT can be referred to in any book on wastewater management.
What is Effluent Treatment Plant
(ETP)?

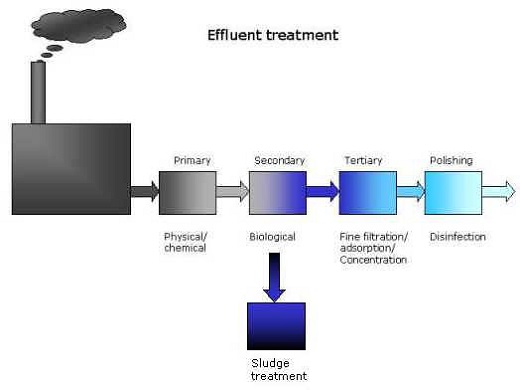
ETP is the effluent treatment plant is used by leading companies, Large hotels, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries to remove the toxic and non-toxic materials or chemicals from the wastewater. In this plant, the treatment of industrial effluents and wastewater is done.
ETP plants use evaporation and drying methods and other techniques such as centrifuging, incineration filtration for chemical processing, and effluent treatment. To prevent the pollution of the receiving water the treatment of effluents is very important.
Faqs
Physical water treatment, chemical water treatment, biological water treatment and sludge treatment.
Aerobic process, anaerobic process and composting.
Some other articles you might be interested in:
